Surgery Services
Cystoscopy/ Urodynamics in Brooklyn
Cystoscopy/ Urodynamics in Brooklyn
Filling cystometry is the method by which the pressure/volume relationship of the bladder is measured during bladder filling. It is used to assess detrusor activity and bladder sensation, capacity, and compliance. Cystometry can be done with one channel measuring bladder pressure alone or with an additional channel that simultaneously measures abdominal pressure through the rectum or vagina. The advantage of the multichannel test is that it can discriminate between changes in abdominal versus bladder pressure by electronically subtracting the abdominal component from intravesical pressure. Only a multichannel test can show that a rise in bladder pressure is due to detrusor contraction rather than tensing of the abdominal wall. This information is important for avoiding a false impression of detrusor overactivity. As an example, detrusor overactivity during single channel cystometry is not reproducible by multichannel testing in 40 percent of women. Thus, most, but not all, experts believe that the multichannel test result is the most reliable for evaluating women with incontinence.
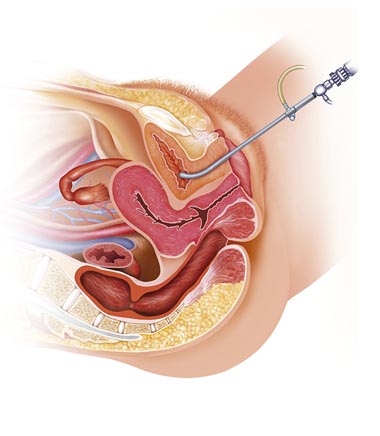
FAQ for Cystoscopy/ Urodynamics in Brooklyn
What Is Urinary Incontinence?
“Urinary incontinence” is the medical term for when a person leaks urine or loses bladder control. Often it is called just “incontinence.”
Incontinence is a very common problem, but it is not a normal part of aging. If you have this problem, you do not have to “just live with it.” There are treatments and things you can do on your own to stop or reduce urine leakage.
There are different types of incontinence. Each cause different symptoms. The 3 most common types are:
- Stress incontinence – People with stress incontinence leak urine when they laugh, cough, sneeze, or do anything that “stresses” the belly. Stress incontinence is most common in women, especially those who have had a baby.
- Urgency incontinence – People with urgency incontinence feel a strong need to urinate suddenly. Urgency incontinence is also known as urge incontinence. Often the “urge” is so strong that they can’t make it to the bathroom in time. (If you have these sudden urges but do not leak urine, you might have an “overactive bladder.” That can also be treated.)
- Mixed incontinence – People with mixed incontinence have symptoms of both stress and urgency incontinence.
Yes. Here are some steps that can help reduce urine leaks:
- Reduce the amount of liquid you drink, especially a few hours before bed.
- Cut down on any foods or drinks that make your symptoms worse. Some people find that alcohol, caffeine, or spicy or acidic foods irritate the bladder.
- If you are overweight, lose weight.
- If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar as close to normal as possible.
- If you take medicines called diuretics, plan ahead. These medicines increase the need to urinate. Take them when you know you will be near a bathroom for a few hours.
These techniques can also help improve bladder control:
- Bladder retraining – During bladder retraining, you go to the bathroom at scheduled times. For instance, you might decide that you will go every hour. You would make yourself go every hour, even if you didn’t feel like you needed to. And you would try to wait until a whole hour had passed if you needed to go sooner. Then, once you got used to going every hour, you would increase the amount of time you waited in between bathroom visits. Over time, you might be able to “retrain” your bladder to wait 3 or 4 hours between bathroom visits.
- Pelvic muscle exercises – Pelvic muscle exercises strengthen the muscles that control the flow of urine. These exercises can help, but people often do them wrong. Ask your doctor or nurse how to do them right.
Yes. Your doctor or nurse can find out what might be causing your incontinence. He or she can also suggest ways to relieve the problem.
When you speak to your doctor or nurse, ask if any of the medicines you take could be causing your symptoms. Some medicines can cause incontinence or make it worse.
The treatment options differ depending on what type of incontinence you have, and whether you are a man or a woman. Some of the treatment options include:
- Medicines to relax the bladder
- Surgery to repair the tissues that support the bladder or to improve the flow of urine
- Electrical stimulation of the nerves that relax the bladder
Many people with incontinence can regain bladder control or at least reduce the amount of leakage they have. The key is to speak up about it to your doctor or nurse. Then work with him or her to find an approach that helps you.
Request Your Consultation Now
If you would like to learn more about Cystoscopy/ Urodynamics in in Brooklyn, fill out the form below to consult with our doctors.








